After the RTX 50 Series AIB graphics cards are widely poking and expanding, the Tech Dimgod Egor Walvasic of the Egor Lab has been discovered that are likely there. About Hotspot on many RTX -50 Series AIB Partner Cards.
It seems that these hotspots are mainly and mostly directly produced due to the power supply components being close to each other on the PCB and connecting to a very low marks, though it seems that at least some of this density can be the result of NVIDIA guide for board partners.
The reason is that, according to Egor, which refers to the RTX 40 series thermal design guide for the RTX 40 series, which stands for people with NDARTX 50 series, the guide is “very wrong and incomplete”, especially about the specific area where the hotspot is on.
Although two cards in Focus are the Palest Jeffour RTX 5080 gaming pro and PNY Jeefor RTX 5070 OC, Agor claims that hotspot can be seen on more cards than them. It can also be seen at the same place on the “Various Conditions of Big Board Partners Cards such as Pallets, PNY and MSI, as well as other manufacturers.”
Even it can be “on cards that look irrational in terms of performance at first glance, such as RTX 5060 TI” because “even only 180 watts of powers can be affected if the toopology is focused on only some supply stages and the problem is maintained.”

So what is the problem? Basically-and to simplify something that Igor has explained in great detail-the PCB of these 50 series is designed in such a way that densely-filled VRMS concentrates the heat generated from high current flow in a small area. This is not just about having very little VRM, either, especially it is made clear that the ves (vertical contacts through PCB) pass through copper power planes. They are closely rooted together, resulting in lack of vertical temperature consumption.
This leads to hotspot, which Igor identified. He tested the RTX 5080, the temperature reached more than 80 ° C and he tested in RTX 5070, reaching more than 107 ° C. Although this temperature may not cause immediate volatility, the problem is that it will not be good for long -term stability. Egor says:
“The current carrying routes are often reached the limit of thermal and electricity specification, which has no additional path to aging, manufacturing variations or burden peaks. As a result, the structures that work reliably under ideal conditions, but are reliably -sensitive.
The key phrase here is “under ideal conditions”, and it has a potential criticism of NVIDIA thermal design guide and a potential reason for this hotspot problem.
The Thermal Design Guide is the one that gives NVIDIA AIB partners, cooler developers, etc., to compare the thermal planning of various components to compare the language. According to Igor, the RTX 4090 Thermal Design Guide, using an example, has some problems using NVIDIA guide or AIB partners.
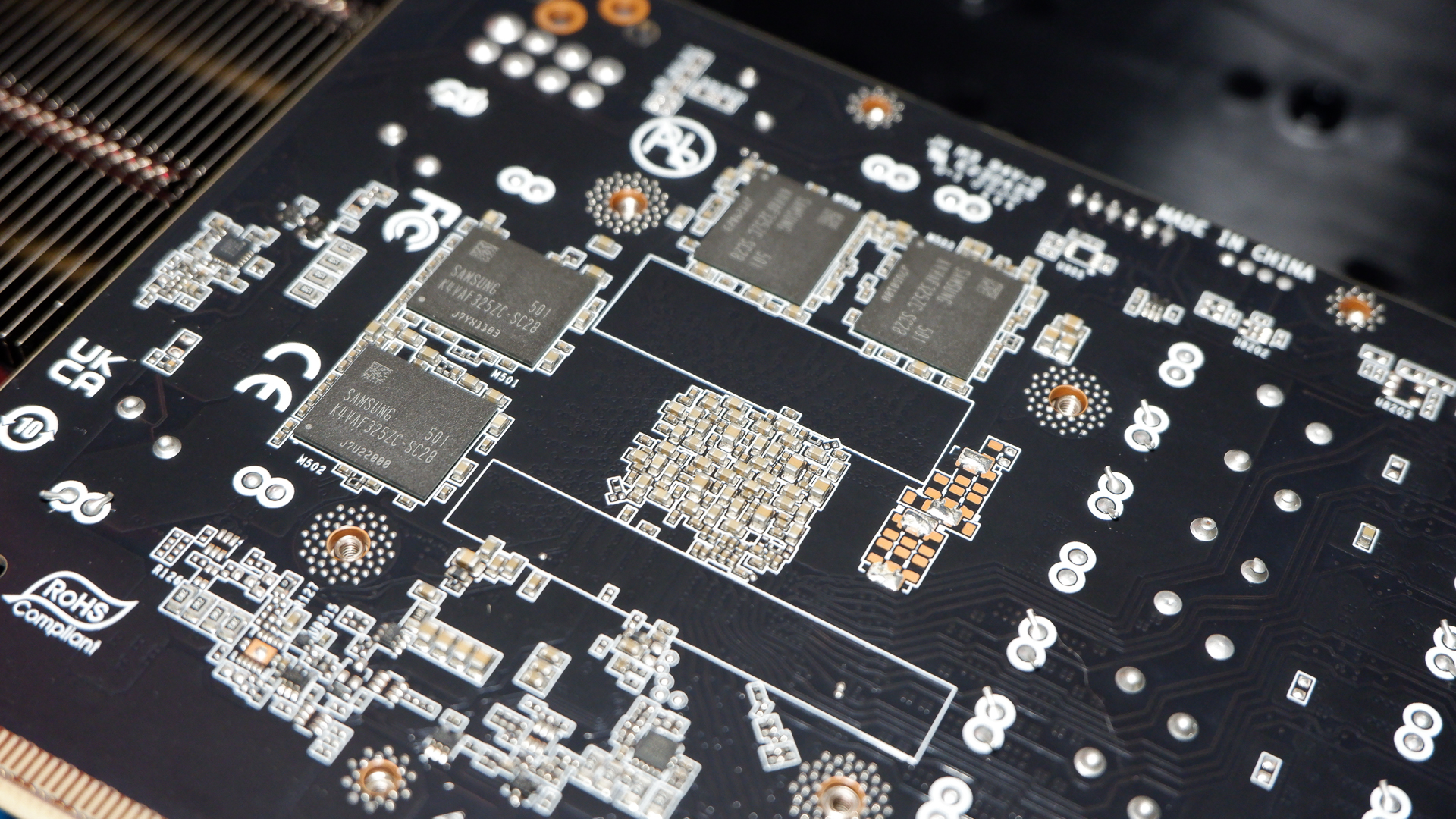
The main problem is that “many parameters are ideal assumptions that are practiced through various impressive factors.” In other words, its standards do not apply to the use of the real world, at least not to endanger thermal problems. In fact, he presses the house at the point he pointed out of which he said: “It is noteworthy that this particular area has not been highlighted as an important area on its own in the official thermal design guide.”
Igor has also shown that there will be no need to solve the problem. In the back of the graphics card to help eliminate heat, where hotspots are located, “thermal relief” (thermal pad) needs to be made.
Such a solution is something in which cooler manufacturers may know about this problem for these graphics cards. Which is probably something that, thermal design guide, should have been alerted to them and may have been aware of them.
Like most things in the industry, although, it is rarely easy to identify the reasons for the root. Egor has indicated from the beginning that there are several types of actors involved in the preparation of the graphics card, and in fact it may be poor communication and cooperation among various actors that can cause such problems.
“Layout managers in board partners often rely directly to outdoor PCB suppliers and have to adapt their designs to a cold solution, which in turn is formed under the separate design and manufacturing complexes, which is the result of the current impact of the current name – the impact of these issues. There are those who include that none of them can be included so that any of them can be included. “
Many cooks can spoil a broth, maybe?
Whatever the case, I will not worry too much about your RTX 50 Series GPUs yet. This type of temperature should not cause short -term problems. There is more concern that GPU’s life can be shortened in a few years.
Of course this is not great, but you don’t have to worry about melting your graphics card at any time soon because of any of these hotspots. I’m probably more worried about these power cables …
