GPU companies, such as AMD and NVIDIA, spend a large amount of money every year to research rendering techniques, either as part of the design of future architecture to improve the performance of their chips. A recently approved patent suggests that the AMD began searching for the use of nerve networks in ray tracing at least two years ago, only when the Redon RX 7000 series was about to be announced.
Under the invasive name of the ‘Patent Application 20250005842’ of the United States, the AMD submitted a patent application for a neural network -based ray tracing in June 2023, with a rubber seal of approval in January this year. This document had a stand by one Anand Tech Forum The user (through dsogaming And reddit) With a troupe of other patents, the method of covering work items and BVH lasi geometry compression -based BVH (Bounding Volume Hyrerich).
Nerve network patent caught my focus on the most, though one of the reasons is that While It was presented for approval and partially because this procedure requires undoubtedly the use of cooperative vectors. An extension of Directorate 3D and Wilkan has been announced recently, which allows shader units to directly take action on the matrix or tanker units.
What this process actually does is determine if a ray of camera is found in a 3D scene by something from which it is found. It starts as a BVH Terurel, working through the geometry of the scene, to see if there is any interaction between a ray and a box. Where there is a positive result, then this process “Find a feature vector using the modified polar coordinated.” Feature vector Machine is something to learn. A numeric list of items or activities is being tested.
The shader unit then runs a small nerve network, which is the feature vector input, and there is no decision out of the ray as an output.
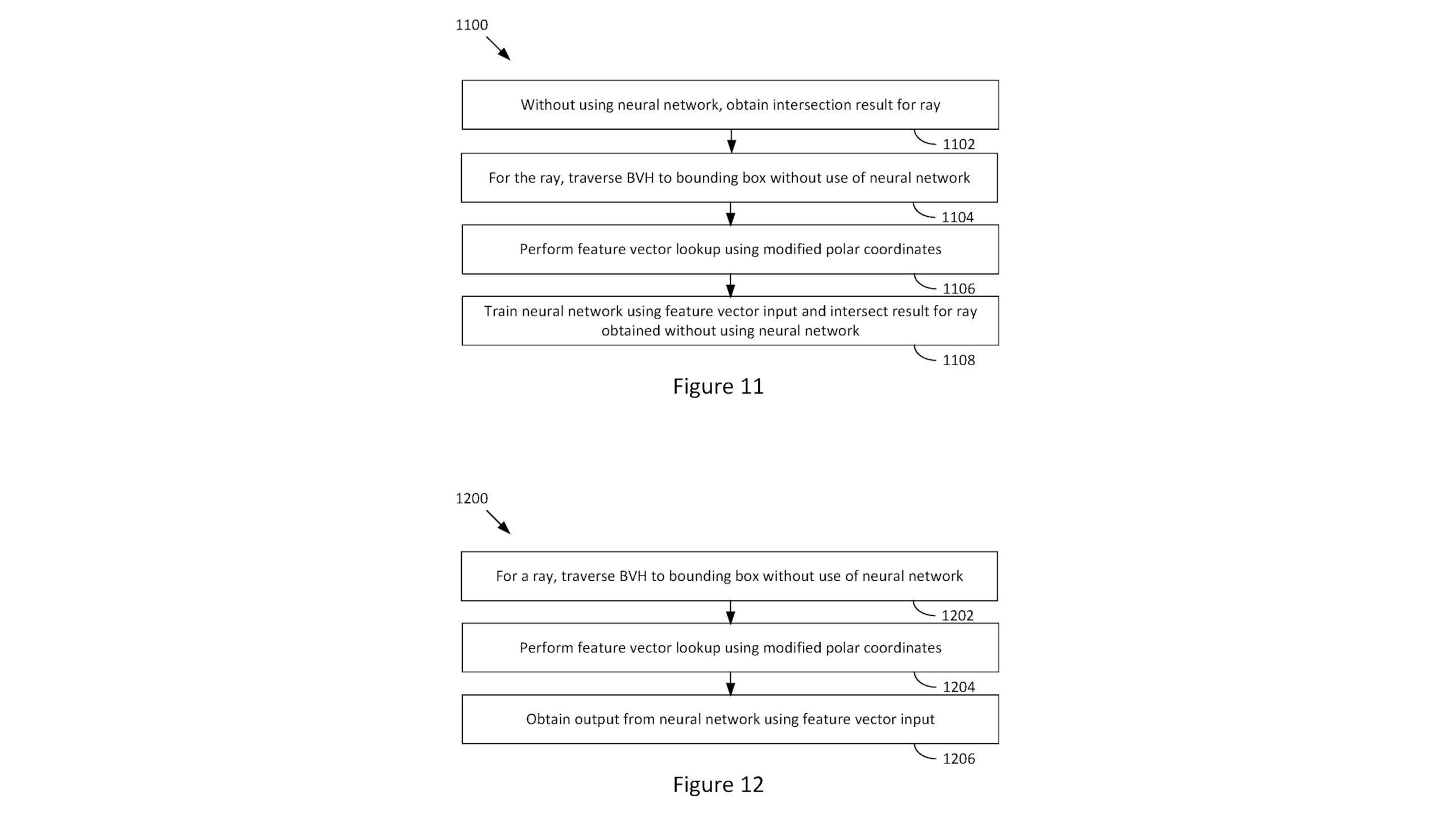
Perhaps all of this does not look too much and, the truth may not be told, it may not be, but the thing is that the AMD has been clearly apparently apparently implemented in researching ‘nervous rendering’, long before NVIDIA had a major uproar about it with the issuance of its RTX 50-series GPUs. Of course, this is normal in GPU research. The initial chip design takes years to go to a shelf product, and if the AMD has just begun to do such research, it will be ridiculously far behind Nvidia.
And do not fool the patent submission date. In June 2023, only when the US Patent Office received a request and it has no choice that the AMD sent it all together next week. In other words, Team Red has been studying it for many years.
Back in 2019, a AMD patent for hybrid -ray tracing procedure On the scene, which was presented in 2017. Although it is not easy to determine whether its use was ever described, RDNA 2 architecture used a similar setup and launched at the end of 2020.
Patent documents never bother himself with real performance, so there is no suggestion that you are looking at a small nerve network running a radian RX 9070 XT at any time at any time (mostly because it is more than 3D, but if it is more than 3D, it is more than 3D). And it is part of the share and part of the parcel, which is part of the parcel and is part of the parcel and part of the parcel, which is part of the 3D Pressal and was part of it and part of it, whose share was part and parcel, whose share was part and parcel, whose share was part and parcel and parcel. Apply in hardware or sports.
Making chips with billions of more transistors and hundreds more shader units is becoming more expensive than the actual benefits in real -time performance. AI offers a potential route around this problem, which is why RDNA 4GPU Games have dedicated matrix unit to handle such things
At the end of the day, it is just a bunch of numbers changing in beautiful colors on a screen, so if AI can run faster or look better or even better, or even better, then it is not difficult to see why the AMD’s choice is spending so much time, trying and rendering money on AI research.
